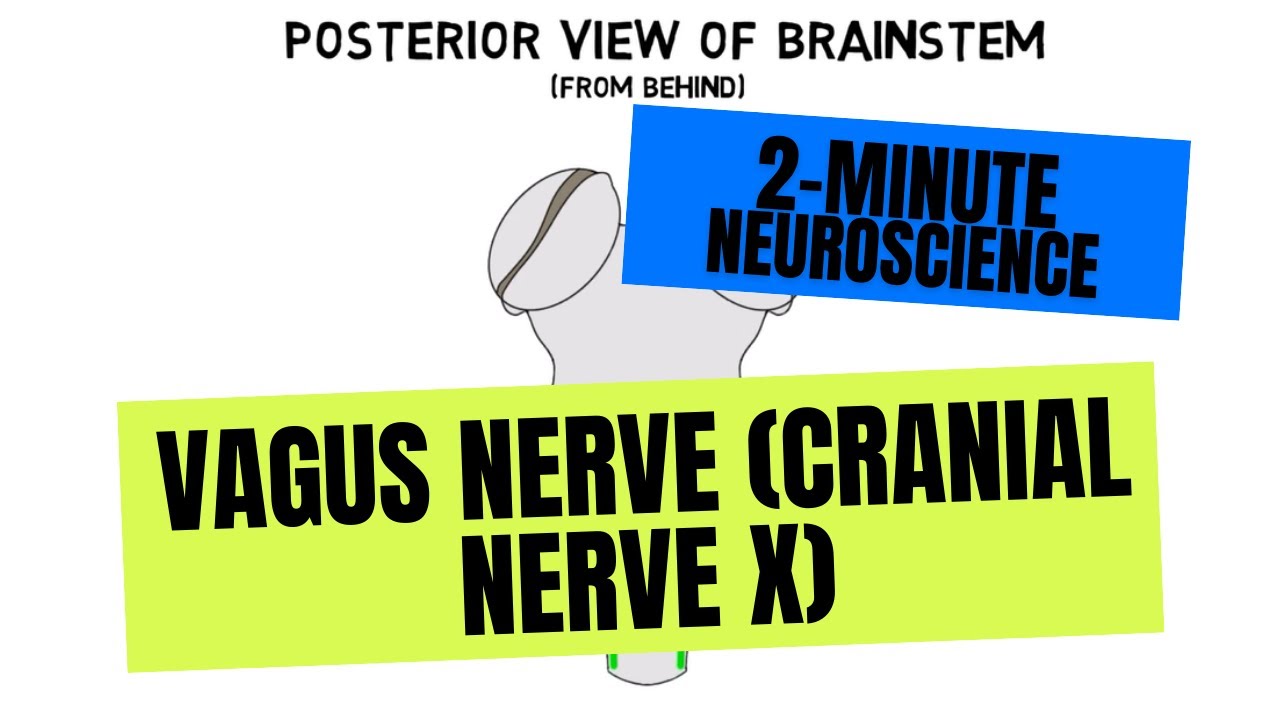
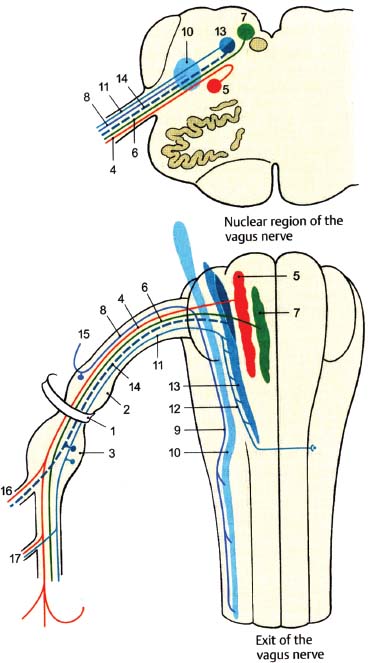
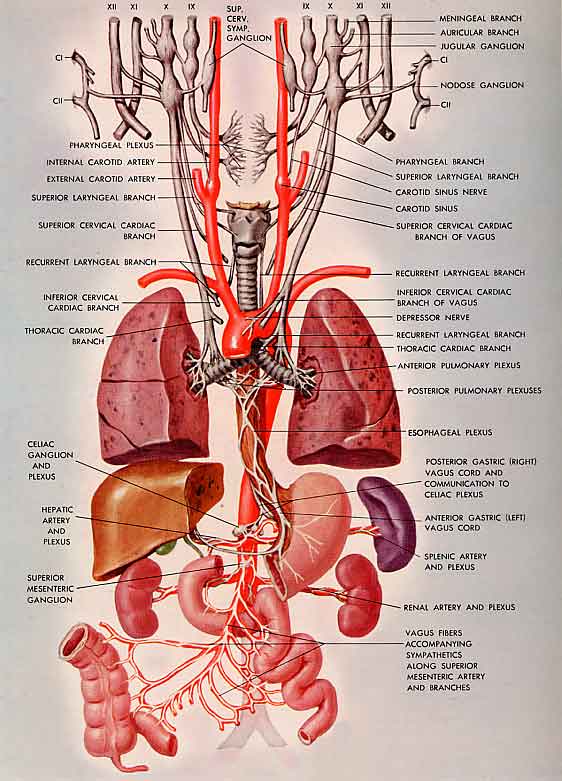
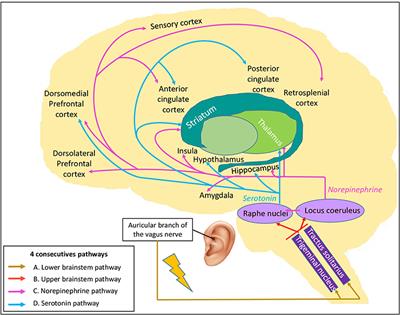
Vagal Nerve Pathway

The vagus nerve trunk subsequently passes down the neck between the carotid artery and the internal jugular vein within the carotid sheath.
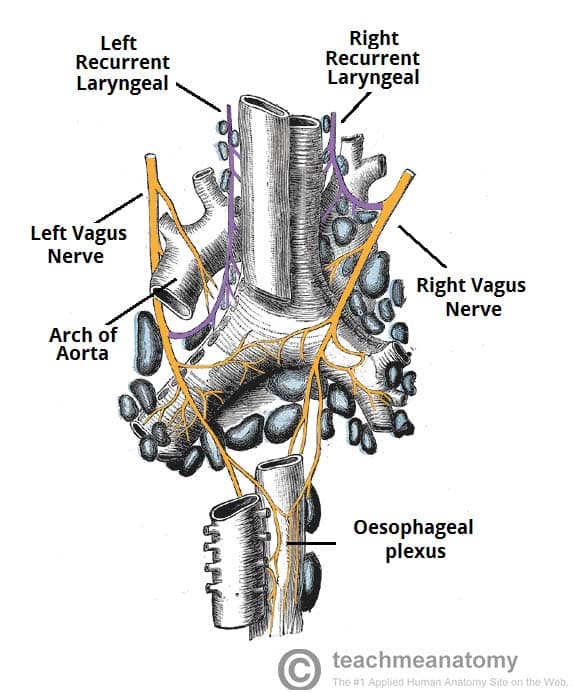
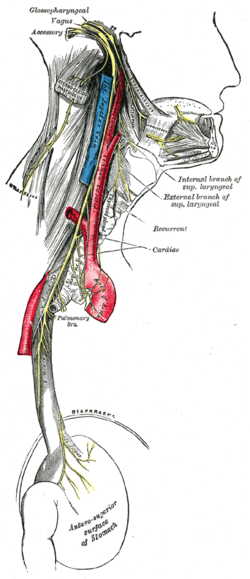
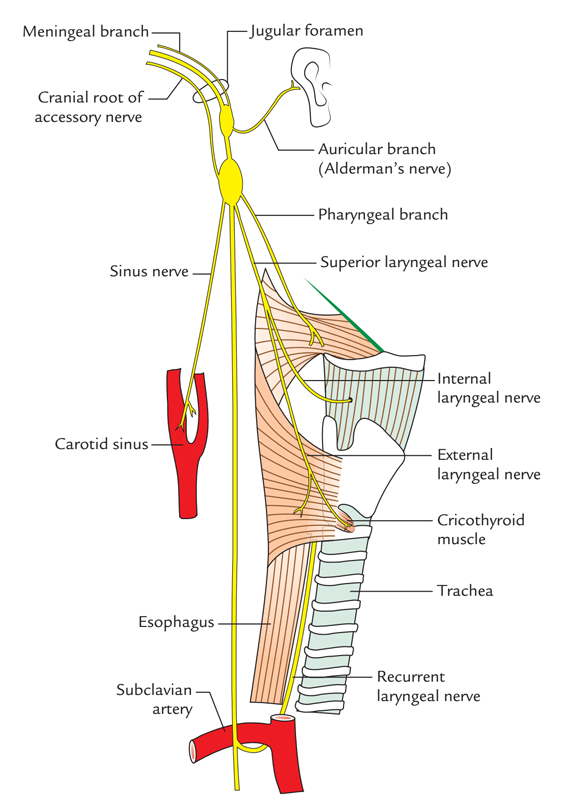
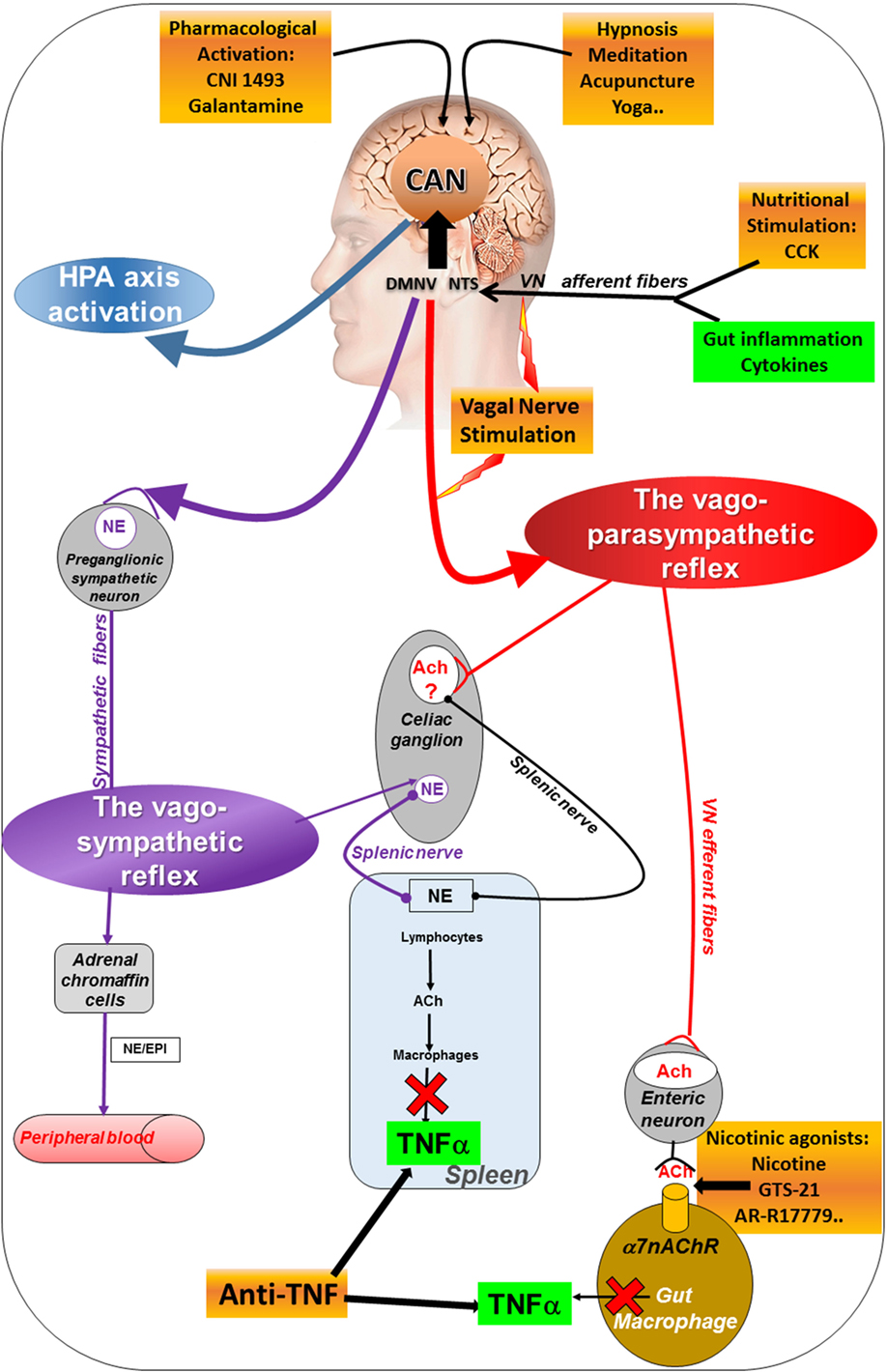
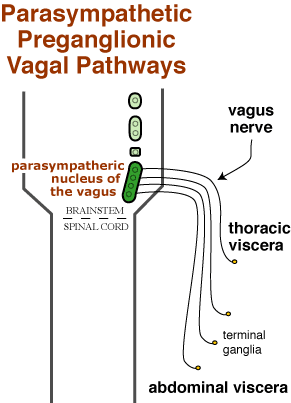
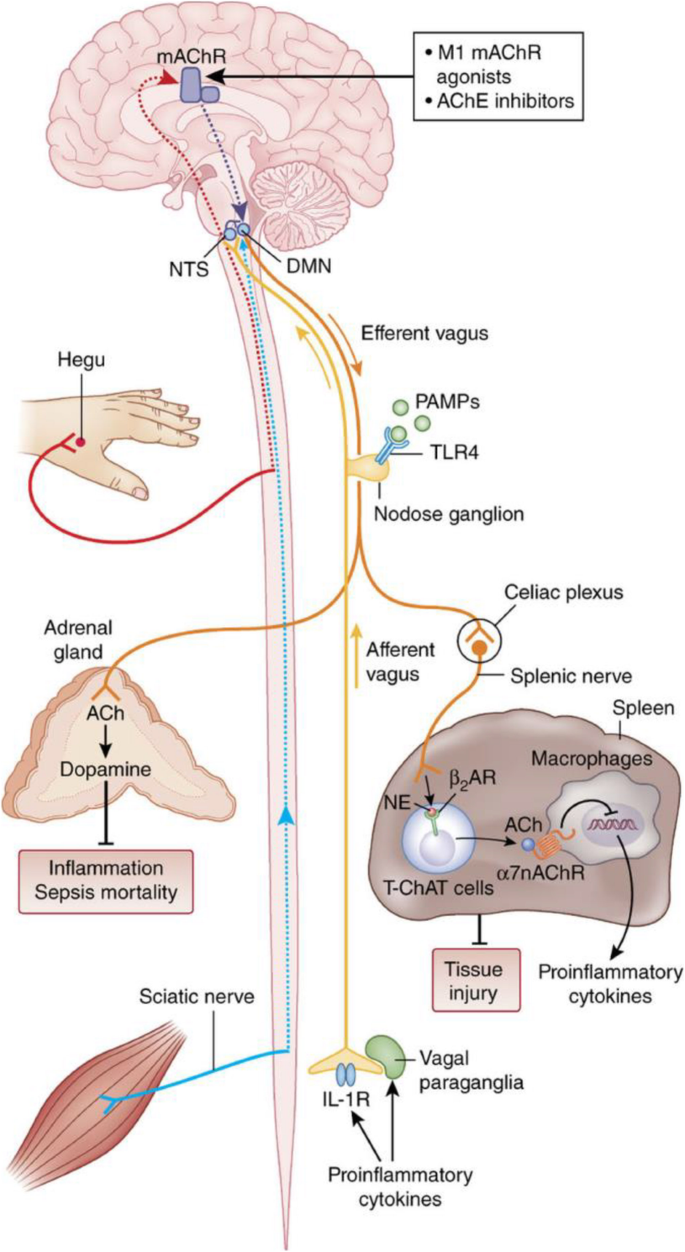
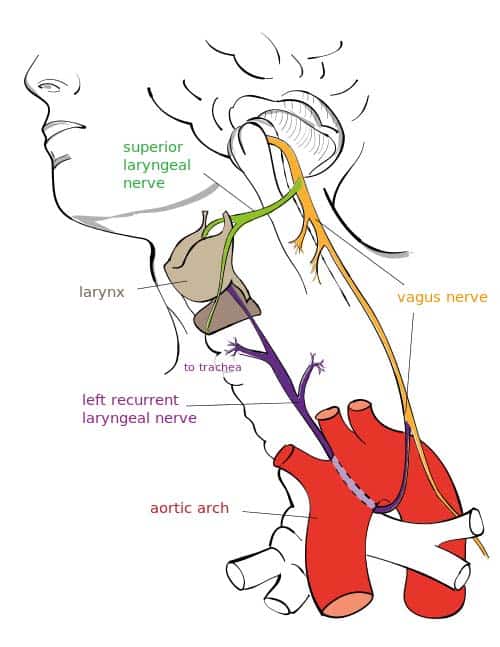
Vagal nerve pathway. The right vagus nerve passes anterior to the subclavian artery and posterior to the sternoclavicular joint entering the thorax. Vagus nerve anatomy and function the word vagus means wandering in latin. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus. Modern medicine treats individual organs as the area of disease and ignores the fact that your brain and nervous system tell your organs what to do.
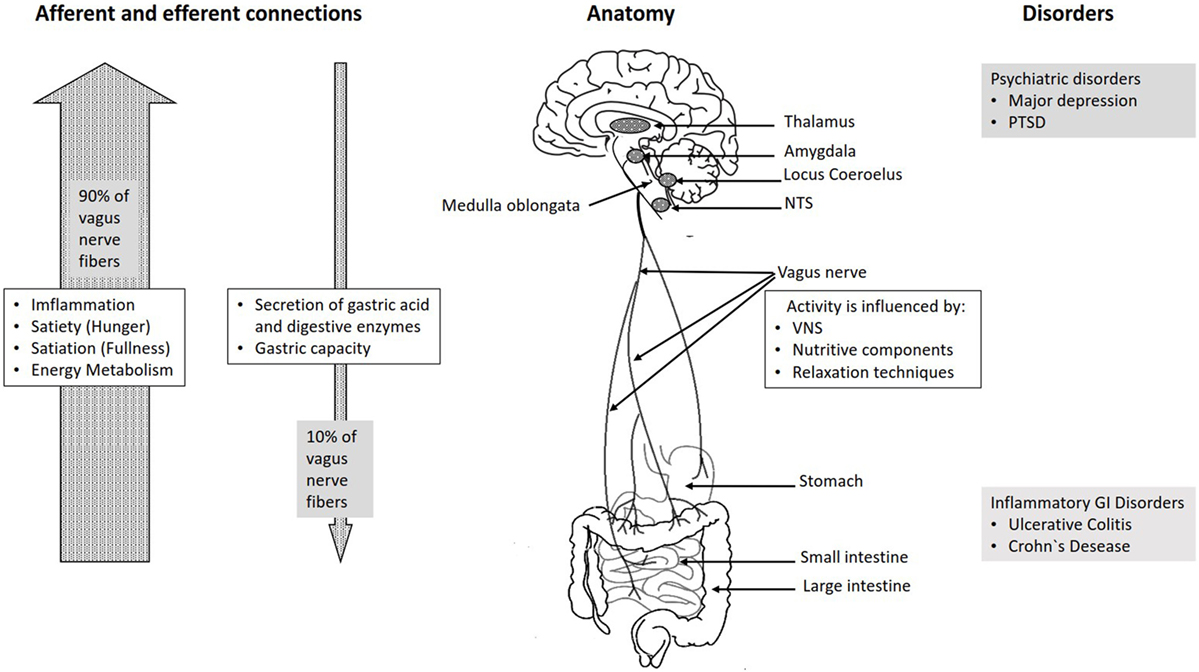
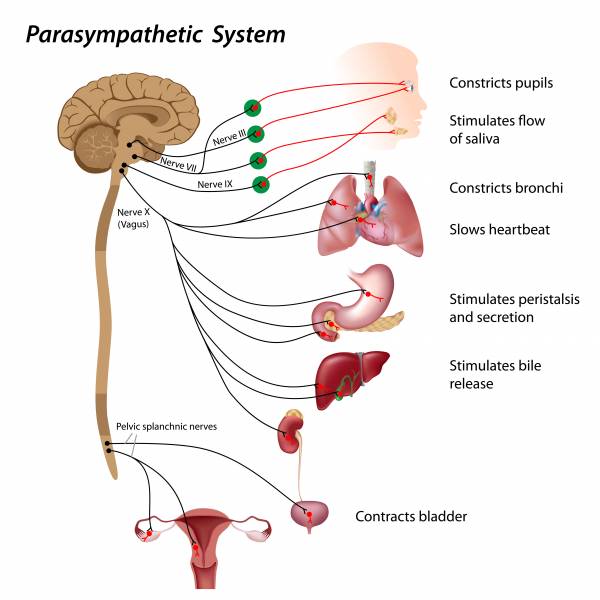
In the cervical area it rides along with the common carotid artery and internal jugular vein. It is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises sensory and motor fibers. It stems out from the medulla oblongata and spreads out to the neck chest and abdomen. The vagal pathway is a system of nerves that connects outward from the brain and regulates many organs in the body the heart lungs gut liver and more.
The vagus nerves are normally referred to in the singular. At the base of the neck the right and left nerves have differing pathways. This is a very appropriate name as the vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve. In the neck the vagus nerve passes into the carotid sheath travelling inferiorly with the internal jugular vein and common carotid artery.
At the base of the neck the nerve enters the thorax however the right and left vagus nerve take different paths after this point.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-vagus-nerve/XUEL9xoLytxotGnVM3dw_Kn3w9HwgpbYnrxaAy0LoJQ_N._vagus_01.png.jpeg)